[ad_1]
PM Photographs
When the COVID-19 pandemic hit america in early March 2020, the Federal Reserve (FED) swiftly responded to restrict the financial fallout. It adopted a spread of measures, together with lowering its rate of interest goal to close zero and implementing large-scale purchases of U.S. Treasury bonds and mortgage-backed securities (MBS). These actions, often called quantitative easing (QE), concerned injecting reserves into the banking system. Because of these purchases, the Fed’s stability sheet grew from round $4 trillion previous to the pandemic to almost $9 trillion by the start of 2022.
Quantitative Easing vs Tightening
QE had first been employed by the Fed greater than a decade in the past as an unconventional financial coverage instrument throughout the Nice Recession. Nonetheless, its return throughout the COVID-19 disaster means that it has change into a extra routine a part of the Fed’s disaster toolkit. However, economists proceed to debate the effectiveness of QE and have restricted information in regards to the reverse technique of shrinking the Fed’s stability sheet, often called quantitative tightening (QT).
In response to inflation working nicely above its long-term goal, the Fed started unwinding its accommodative financial coverage in 2022. This concerned ending QE in March and commencing QT in June. When QE concluded, the Fed reinvested any maturing securities to keep up the scale of its stability sheet. With QT, the Fed ceased reinvesting as much as $30 billion in maturing Treasuries and $17.5 billion in maturing MBS every month, thereby passively shrinking its property as these securities matured with out being changed. The caps on reinvestments then elevated to $60 billion and $35 billion, respectively, in September 2022.
FRED Knowledge vs SPY Worth (Google sheets chart)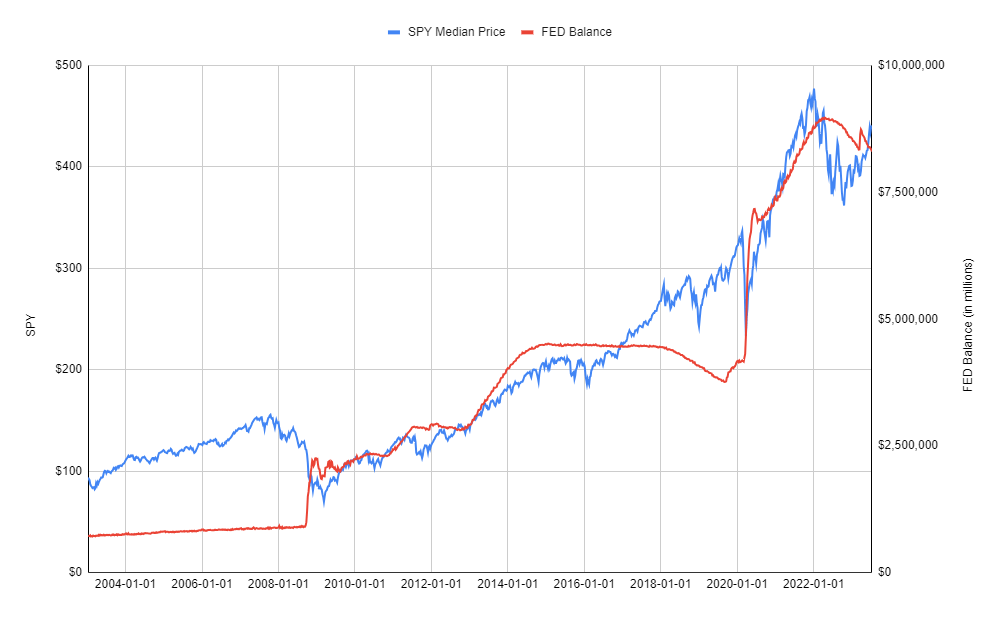
The first objective of QE is to scale back long-term rates of interest. By shopping for long-term property, the Fed reduces their provide, thereby rising their value and decreasing their yield. Decrease rates of interest can stimulate financial exercise by lowering the price of borrowing. Whereas some financial fashions recommend that QE ought to have little impact because it swaps one kind of presidency legal responsibility for an additional, there are different theories that specify the way it stimulates the financial system. As an example, sure monetary companies might have preferences for holding long-dated securities, and QE may present a sign about future Fed coverage and enhance liquidity circumstances in monetary markets.
In distinction to the debates surrounding QE, there may be significantly much less certainty relating to the consequences of QT. The Fed’s expertise with shrinking its stability sheet is restricted to the earlier episode from 2017 to 2019, and even then, the obtainable empirical proof is scarce. A current research by economists on the Fed Board of Governors estimated that lowering the stability sheet by roughly $2.5 trillion over a number of years could be roughly equal to elevating the Fed’s coverage price by half a proportion level. Nonetheless, the authors emphasised the appreciable uncertainty related to this estimate.
One key distinction between QE and QT lies of their signaling results. QE usually entails a swift and considerably stunning response by the Fed throughout monetary crises, which helps reassure markets. In distinction, the Fed has been cautious with QT, offering ample advance discover and following a set schedule to keep away from market surprises. The Fed’s method to QT displays its want to focus market consideration on the federal funds price as the first financial coverage instrument. Whereas QT might not produce vital announcement results like QE, it has been discovered to have stronger liquidity results.
Shrinking the stability sheet by means of QT serves a number of functions. It offers further financial tightening to carry inflation again to the Fed’s 2 p.c goal. Moreover, it helps mitigate the rate of interest danger confronted by the Fed because it raises charges. When the Fed tightens financial coverage and will increase the curiosity it pays on reserves, it dangers paying out extra on its liabilities than it earns on its property since charges on liabilities will rise whereas charges on property stay largely fastened. Shrinking the stability sheet reduces the chance of the Fed recording losses and enhances the credibility of its financial coverage.
Furthermore, the composition of the Fed’s property is another excuse for implementing QT. The Fed holds a major quantity of MBS, however its plan for lowering the stability sheet expresses a long-term choice for holding primarily Treasuries. Policymakers and economists argue that selections relating to the allocation of credit score to totally different sectors of the financial system must be made by Congress or the Treasury Division, moderately than the Fed. Nonetheless, reaching a Treasuries-only stability sheet might take time, because the tempo of MBS maturing and rolling off the stability sheet relies on mortgage charges and house owner refinancing exercise.
Lastly, partaking in QT permits the Fed to unencumber capability for future QE throughout crises. If the Fed’s stability sheet continues to broaden indefinitely, it may probably exhaust the availability of acceptable property to buy for QE. Subsequently, by implementing QT, the Fed ensures that it has room to maneuver and make use of QE as a counter-cyclical coverage instrument when essential.
Because the inventory market undergoes a restoration from the earlier bear market, there are lingering dangers that would hinder its progress. Considered one of these dangers is the potential impression of upper rates of interest, in addition to the potential of earnings disappointments. Nonetheless, a extra distinct and evident danger arises from the draining of liquidity within the world banking system from QT.
Liquidity Dangers
The S&P 500 (SPY) has proven a substantial enhance of roughly 27% since hitting a low level in early October. This vital rally has led to rising requires a correction, because the index has change into dearer, with a price-to-earnings ratio of 19 instances mixture ahead earnings-per-share estimates in comparison with 15 instances at the start of the rally. Traders are hopeful that the Federal Reserve will quickly stop climbing rates of interest, which might stabilize the financial system and facilitate company revenue development. Nonetheless, the impression of already elevated rates of interest tends to manifest with a delay, probably leading to disappointing gross sales and earnings for firms. If the Fed maintains larger charges for an prolonged interval moderately than lowering them, these issues may materialize. However, constructive financial institution earnings reported not too long ago recommend that earnings will not be presently impeding the market.
Amidst these dangers, the connection between the inventory market and world liquidity emerges as a vital issue that would impression inventory efficiency. The worldwide M2 cash provide, encompassing money in checking and financial savings accounts, in addition to money-market-fund property, has remained stagnant 12 months over 12 months, following a 5% decline in 2022, as reported by Morgan Stanley. Central banks have elevated rates of interest by promoting property, thereby extracting money from the banking system and lowering the amount of cash obtainable for lending and spending. Consequently, merchants and portfolio managers discover themselves with diminished funds.
Contemplating the traditionally shut correlation between the M2 cash provide and the S&P 500, Morgan Stanley means that the index theoretically must be located someplace between 3700 and 3800. This projection implies a possible 15% decline from the present ranges.
TradingView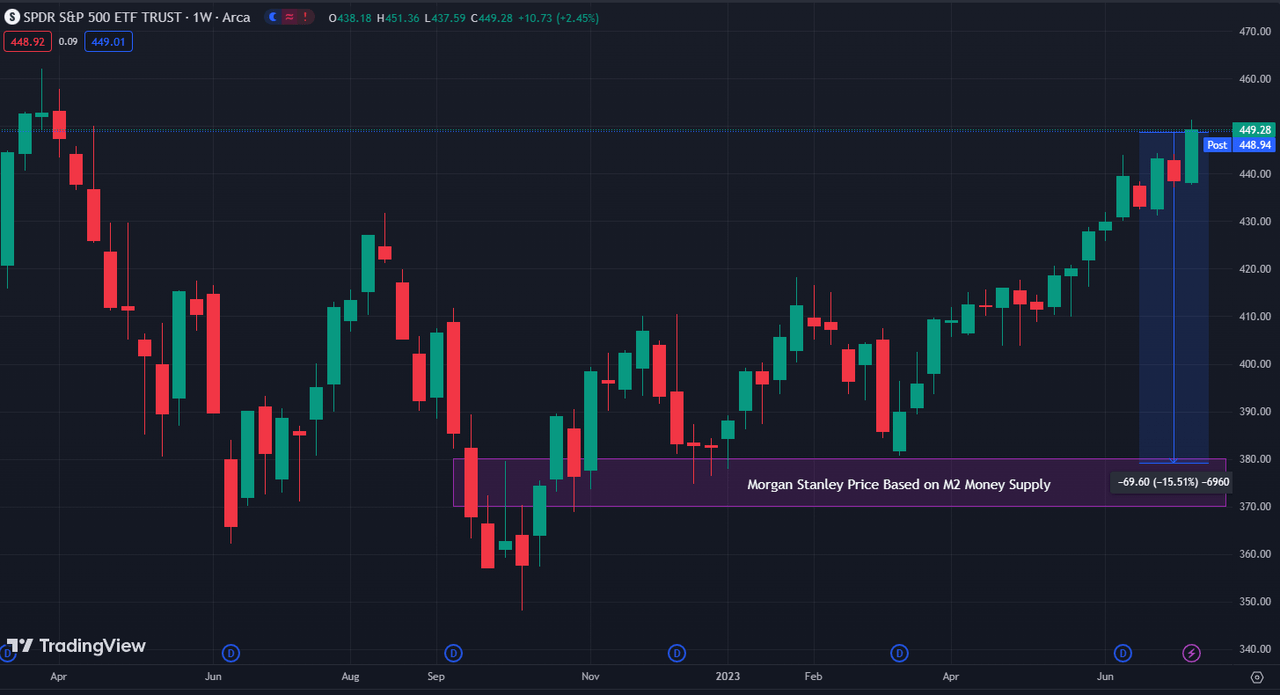
Though such a pointy drop could seem inconceivable given the market’s consciousness of the liquidity drain brought on by central banks, you will need to acknowledge the reasoning behind Morgan Stanley’s evaluation. Regardless of expectations of decrease liquidity ranges, the mechanics of getting much less cash inside the system may have an antagonistic impact on inventory demand. Portfolio managers have already lowered their money holdings as they capitalized on shopping for shares over the previous a number of months. Moreover, customers might ultimately curtail their spending as they exhaust their money reserves, even when this impression has but to be mirrored in second-quarter earnings studies. The Fed’s dedication to stepping in on the first signal of disaster, although, has given the market the arrogance wanted to undertake a risk-on method with the acquisition of shares, particularly within the development sector. Whereas logic might lead you to consider {that a} financial institution of Silicon Valley’s scale collapsing could be an enormous crimson flag for the financial system, the Fed’s fast quantitative easing in response has helped gasoline this rally. The stability sheet has already moved under pre-March ranges however that fast spike in response to SVB’s demise has traders assured that the Fed will step in to avoid wasting the day. However with liquidity falling, there might not be sufficient gasoline to proceed larger.
FRED Knowledge vs SPY Worth (Google sheets chart)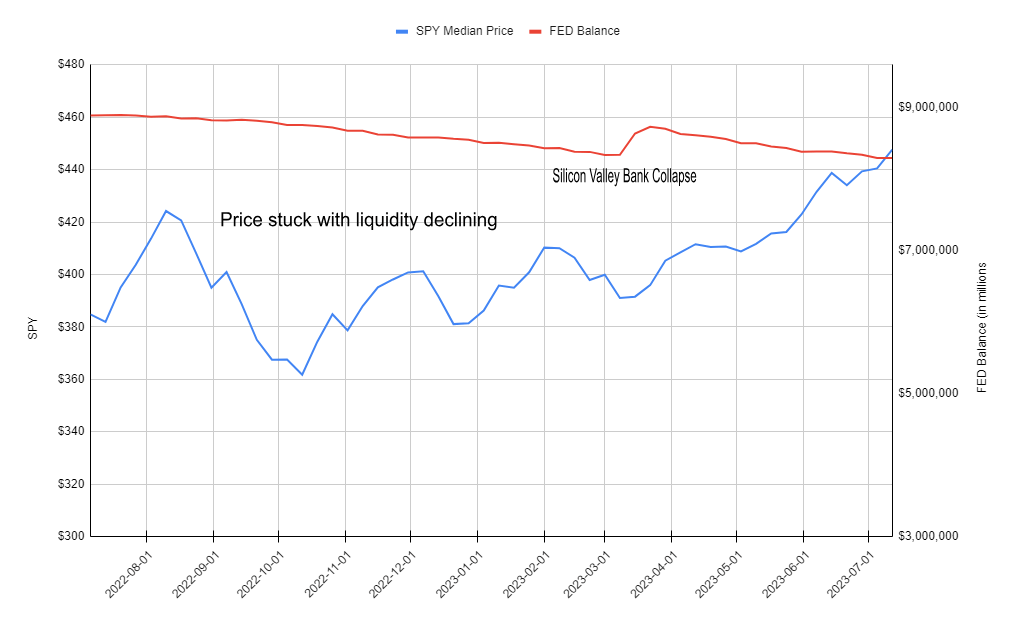
With SPY hitting a yearly excessive and VIX hitting a low, it could be prudent to arrange for the upcoming uncertainties surrounding continued QT with the FED stability dropping under pre-SVB collapse ranges once more. Whereas I feel the smooth touchdown is achievable and am not calling for a market collapse, the current run-up has made draw back safety low cost and having hedges in place (particularly with a robust risk-reward ratio) could be a part of a wholesome securities portfolio.
Commerce Concept
Purchase to Open $410 PUT January 2024 expiration
Promote to Open $405 PUT January 2024 expiration
Max Revenue: ~$443 Max Loss: ~$57
Optionstrat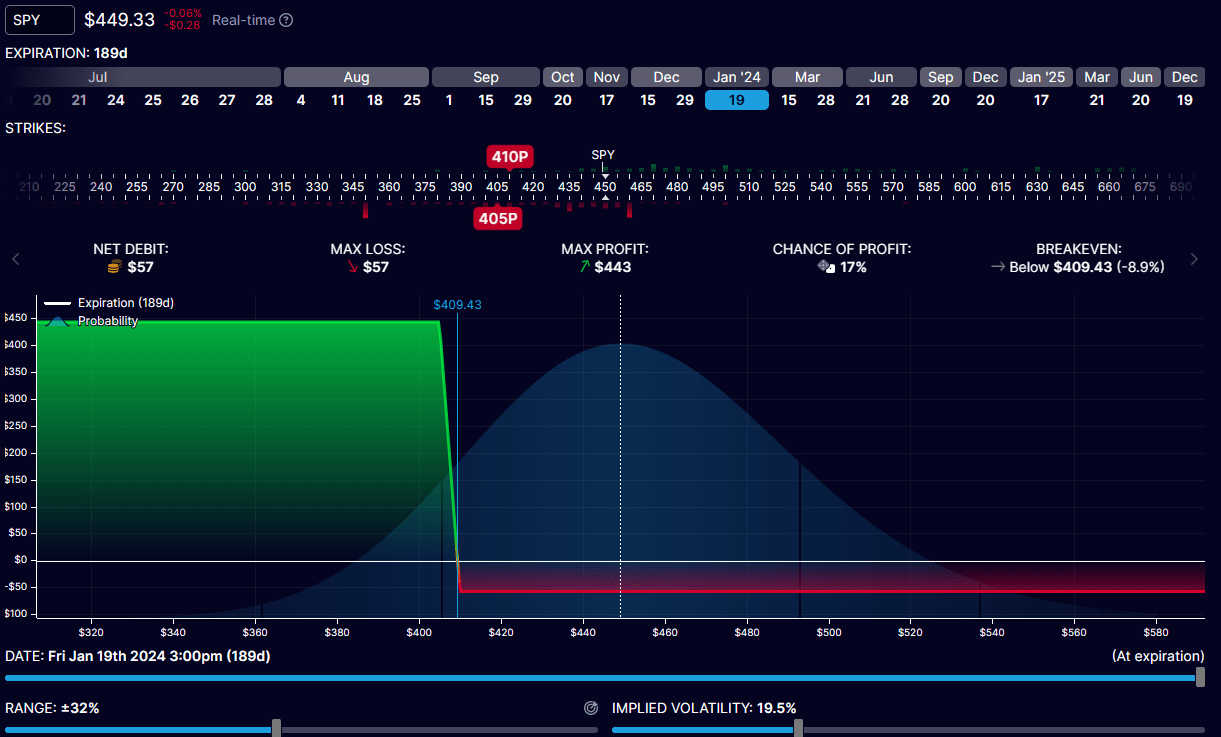
Conclusion
Whereas the inventory market has made vital strides in its restoration from the bear market, it stays weak with the draining of liquidity inside the world banking system, coupled with potential earnings disappointments, are dangers that would affect the market’s trajectory and efficiency. The final perception is that QE has a constructive impact on the financial system, there may be much less certainty relating to the impression of QT on account of restricted empirical proof. The Fed is cautiously implementing QT to realize further financial tightening, scale back losses and rate of interest danger, allocate credit score selections appropriately, and protect capability for future QE. The uncertainties surrounding QT necessitate ongoing analysis and analysis of its results on the financial system.
[ad_2]
Source link



















